 |
Cables
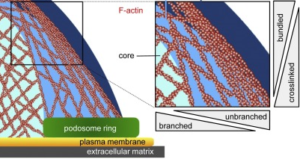
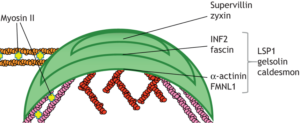
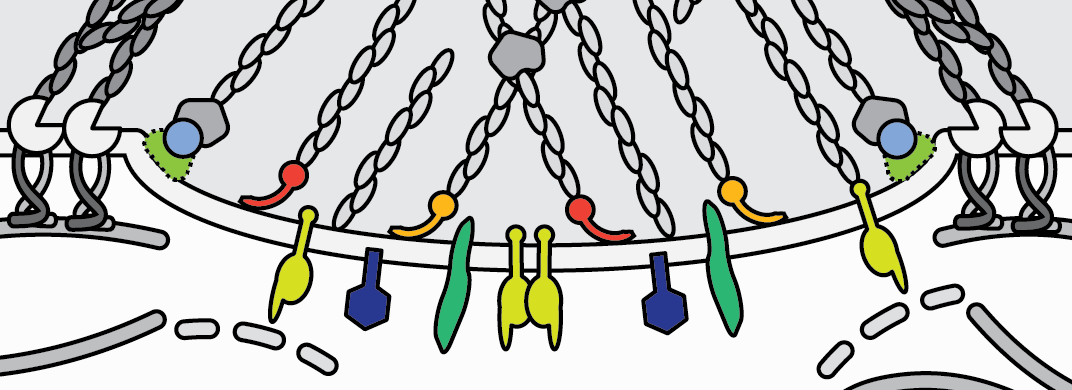
The podosome cables consist of F-actin bundles which are interconnected by myosinIIA. The cables are divided into two different subsets, the lateral and the connecting cables. The lateral cables connect the top of the podosome core with the ring structure and likely transmit the mechanical forces needed to regulate ring protein recruitment. This force is mainly regulated by the polymerization of actin that drives podosome core growth. The dorsal connecting cables link individual podosomes into superstructures like clusters, rosettes and belts. They show a higher accumulation of myosin IIA than the lateral cables and are thus likely more contractile.
|
 |
Base
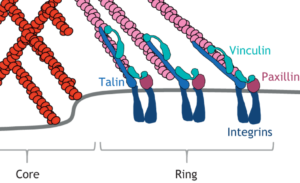
“The ventral region underneath the podosome core that is directly adjacent to the plasma membrane (PM) is now called the “base”. It contains proteins that are associated with the PM through various domains. Currently known components comprise the unconventional myosins Myo1e and Myo1f, which bind phospholipids of the PM (Cervero et al. 2025), transmembrane proteins such as matrix metalloproteinase MT1-MMP (El Azzouzi et al., 2016) and the hyaluronan receptor CD44 (Chabadel et al., 2007), as well as the GPI-linked membrane-bound DNase X (Pal et al., 2021).”.
|